Work Motivation and Job Satisfaction
Introduction
Work motivation and job satisfaction are crucial aspects of organizational behavior and human resource management. These concepts play a significant role in determining employee engagement, productivity, and overall job performance. In this guide, we'll explore the key theories, models, and practical applications related to work motivation and job satisfaction.
What is Work Motivation?
Work motivation refers to the psychological processes that drive employees to exert effort towards achieving organizational goals. It encompasses various factors that influence an individual's willingness to perform tasks and contribute to the organization.
Types of Work Motivation
-
Extrinsic Motivation
- External rewards and incentives
- Examples: bonuses, promotions, recognition
-
Intrinsic Motivation
- Internal drives and personal satisfaction
- Examples: enjoyment of work, sense of accomplishment
-
Social Motivation
- Desire for social interaction and relationships
- Examples: team collaboration, mentorship programs
-
Self-Efficacy
- Belief in one's ability to succeed
- Examples: training opportunities, feedback mechanisms
Theories of Work Motivation
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow proposed that human needs are hierarchical, with lower-level physiological needs forming the base of the pyramid. As these basic needs are met, higher-level psychological needs emerge.

McClelland's Acquired Needs Theory
McClelland suggested that individuals have three types of needs: achievement, affiliation, and power. Each need influences how people behave in organizational settings.
| Need Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Achievement | Desire for success, competition, internal locus of control |
| Affiliation | Desire for friendship, cooperation, external locus of control |
| Power | Desire for influence, control over others |
Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction refers to the degree to which employees find their job rewarding and fulfilling. It encompasses various aspects of work life, including pay, supervision, coworkers, and the nature of the work itself.
Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction
-
Perceived Fairness
- Equity theory suggests that individuals compare their outcomes to those of others
- Examples: salary comparisons, promotion opportunities
-
Organizational Culture
- Shared values and beliefs within the organization
- Examples: open communication policies, recognition programs
-
Work-Life Balance
- Ability to balance professional and personal responsibilities
- Examples: flexible work hours, parental leave policies
-
Job Autonomy
- Degree of independence in performing job duties
- Examples: decision-making authority, skill utilization
Models of Job Satisfaction
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
Herzberg proposed that factors influencing job satisfaction can be categorized into two groups: hygiene factors and motivators.
| Hygiene Factors | Motivator Factors |
|---|---|
| Company policies | Recognition |
| Working conditions | Achievement |
| Salary | Responsibility |
| Supervision | Personal growth |
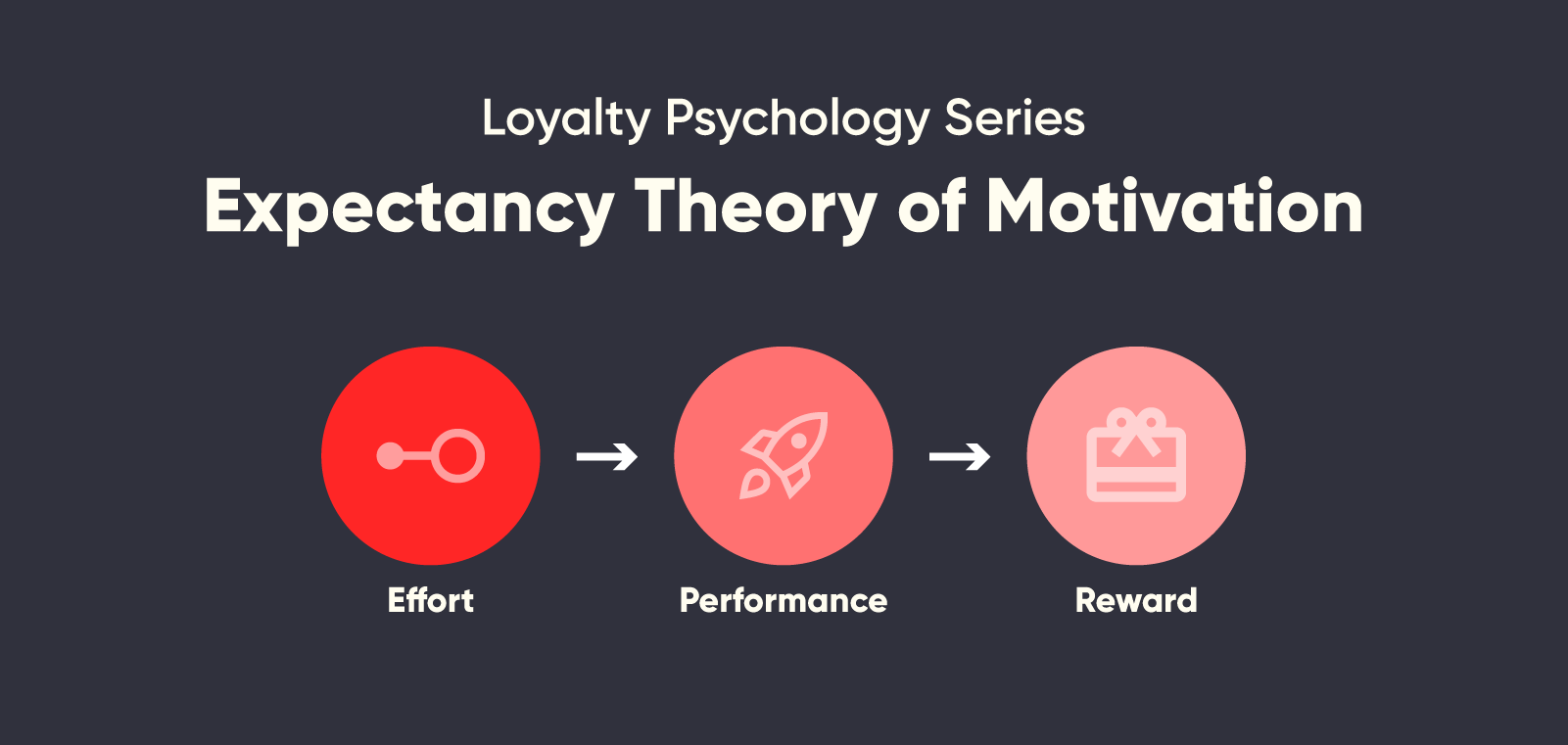
Vroom's Expectancy Theory
Vroom suggested that motivation is influenced by three components: effort, performance, and outcome.
Practical Applications
Employee Engagement Programs
Organizations can implement various strategies to boost employee engagement and motivation:
-
Performance Feedback
- Regular, constructive feedback sessions
- Examples: quarterly reviews, 360-degree assessments
-
Skill Development Opportunities
- Training programs and career advancement initiatives
- Examples: mentorship schemes, leadership development courses
-
Recognition and Rewards
- Public recognition of achievements
- Examples: employee of the month awards, bonus systems
-
Flexible Work Arrangements
- Options for telecommuting or flexible hours
- Examples: remote work policies, compressed workweeks
Conclusion
Understanding work motivation and job satisfaction is crucial for both employees and employers. By recognizing the various factors that influence these concepts, organizations can implement strategies to enhance employee engagement, productivity, and overall job satisfaction. As students pursuing degrees industrial-organizational psychology, it's essential to continue exploring these topics through research, practical applications, and continuous learning.
Remember, work motivation and job satisfaction are dynamic concepts that can change over time. Stay curious, keep learning, and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations to become a skilled professional in this field.